
Why does data segmentation matter?
“The data your company holds is a goldmine of information. With it, you can provide bespoke customer experiences; create more effective marketing segments and campaigns; maximise operational efficiencies and decision making; and even spot future trends and opportunities.
However, if your data is simply collected and left without critical thinking applied, all of that knowledge goes to waste. By segmenting your data into more meaningful divisions, you can gain a deeper understanding of your customers and better understand how to use those insights to full effect.”
What is data segmentation?
Data segmentation is the process of organising and dividing data into smaller, more manageable groups.
By structuring your broad data into groups, you can better analyse it, spot patterns of customer behaviour, and discover emerging trends. These insights can then be used to draw the meaningful conclusions needed to make informed business decisions.
Benefits of data segmentation
- Easier data analysis, helping you identify business risks, trends, and opportunities.
- Better product and service development, driven by clearer insights into customer behaviour and needs.
- More personalised customer experiences, through targeted campaigns, offers, and communications.
- Smarter decision making, with clearer trends and more effective marketing resource allocation.
- Build better training data for your AI initiatives.
Key takeaway
Data segmentation involves structuring your datasets into smaller groups based on shared characteristics or set criteria. This approach replaces working with unorganised information, making it easier for you to understand customer behaviour and make better business decisions.
Common types of data segmentation and their uses
Data segmentation groups your datasets to uncover deeper insights and drive smarter decisions, and by extension marketing segmentation breaks down audiences for more targeted campaigns. Each type of segmentation serves a different purpose and helps answer different business questions.
Behavioural
This divides customers up based on their actions, such as purchase history, website interactions, or social media engagement, and this information can be particularly useful when creating tailored email marketing campaigns. By better understanding the touchpoints a customer has already had with your brand, you can ensure a unique and personalised experience. For example, sharing a product that would work alongside an item they’ve previously bought.
Demographic
This groups customers based on objective information such as their gender, age, ethnicity, education, income, or marital status. This is one of the most common data segmentation variables, and it’s a great option when getting started in sorting your customer useful cohorts.
Firmographic
This grouping is used within B2B marketing and looks at a company’s attributes including their industry, size, and revenue. By looking at an area such as company performance, you can more accurately assess when to reach out with a marketing campaign or offer and with what level of product or service, resulting in better ROIs all round.
Geographic
This splits customers up according to their location, ranging from country, region, and city or whether it’s urban, suburban, or rural. By having a better understanding of a customer’s location, you can create tailored messaging that takes language, culture, climates, seasons, and traditions into consideration.
Psychographic
Sometimes known as attitudinal segmentation, this divides customers up based on their feelings and motivations towards a brand, as well as their interests, lifestyle, attitudes, and values. Consider it the ‘why’ behind their behaviour that can help you create more meaningful marketing that aligns to their core sentiments.
Technographic
This splits customers based on the technology they use, such as device, software, applications, and operating systems. Understanding how a customer is interacting with your brand can help you deliver messaging that’s accessible. If, for example, a customer interacts with the majority of their emails using a phone, you’ll want to consider email content design to ensure your messages can be read comfortably on a small screen, with the most important information front and centre.
Key takeaway
Data can be split according to most characteristics from where your customers live to their job, marital status, or even the types of technology they use. Choosing your segments should directly relate to your business objectives.
Data quality is a segmentation blocker
A 2018 Experian study asked respondents what their biggest challenges to more sophisticated segmentation and personalisation are. Many of the issues relate to the quality and use of data.
47%
said inaccurate data was one of the biggest challenges
40%
said not having enough data was a major issue
42%
also pointed to challenges in accessing information easily
Having not enough data, inaccurate data, or being unable to access that data makes it impossible to properly segment your data and personalise your audience outreach. These issues reinforce the importance of not just collecting data, but also ensuring its quality, accessibility, and structure.
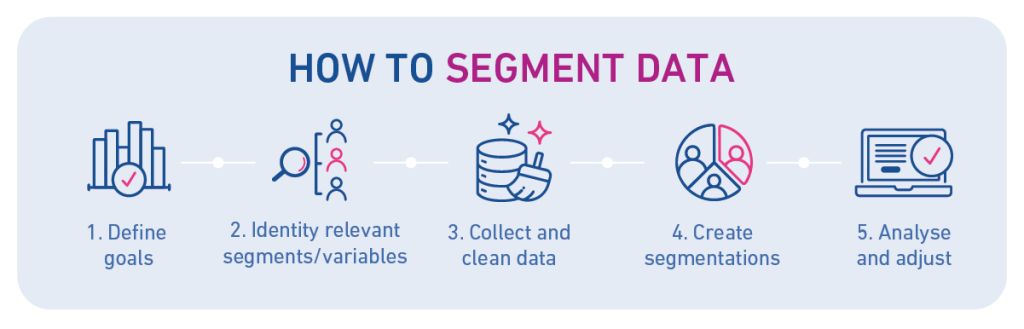
How to undertake data segmentation
1. Define your goals
Start by understanding why you want to group your data and what insights you hope to gain. Are you trying to improve your customer experience or uncover new business opportunities? These goals are likely to change across each department, but it’s important that everyone in the business shares their objectives so you can drill down into the most beneficial data segmentations.
2. Identify relevant segmentation variables
Next comes ‘how’. How will you be organising the data in order to gain the most beneficial insights that are relevant to your goals? Will you be focusing on geographic datasets or behavioural ones? Perhaps you’ll need several types of segmentation for different areas of the business? Depending on your requirements you may need to drill deep into niche datasets. Don’t be afraid to do this as it’s arguably the crux of the data segmentation process: organising data in a specific way for more meaningful insights.
3. Collect and clean your data
After you’ve gathered your data from all relevant sources such as social media, customer databases, and website analytics, it’s time to ensure data quality. High-quality data is an essential component of data segmentation. After all, what use is it to have segmentations if the data within them is incorrect, duplicated, or outdated? There are a range of processes and tools that can help you ensure data quality and validation.
4. Create your segmentations
With all of your cleansed and high-quality data laid out in front of you, you can now group your customer based on the variables you selected in step two. Give each segment a clear name and description, so everyone is on the same page when it comes to the insights gained. You’ll also be able to spot data trends and patterns emerge as the data is grouped together.
5. Analyse and adjust as necessary
The more meaningful your segmentation datasets, the better analysis and more accurate conclusions you can make. Remember, data segmentation isn’t a one-time task. Think of it as a database of evolving information, shifting as new data enters the system or current customer behaviour and trends change. Keep going back to those goals in step one and assess how effective your segmentations have been in helping you achieve them. And, if necessary, adjust them to make sure they remain effective.
Key considerations and best practice
- Data quality and data enrichment is essential for effective data segmentation. Make sure yours is accurate, complete, and up to date.
- Avoid using overly complex or highly specific segmentation. Detail is hugely beneficial in spotting niche trends, but too much can cause confusion.
- Keep analysing, evaluating, and refining your segments based on new data and insights.
- Enriching your customer data with Experian’s reference and enrichment datasets gives you a more detailed and complete customer profile. Once you better understand your customers and have more data attributes to assess, you can better segment and target them.
Key takeaway
To get the most out of your data segmentation start by defining your goals and ensuring you’re working with high-quality datasets. From there, you’ll be able to create meaningful groups that can be analysed and refined.
How can we help?
Data segmentation helps you understand your customer in greater detail. With more meaningful insights into their behaviours, location, and lifestyle you’re better placed to provide enhanced experiences and create more effective marketing campaigns. Both of which can positively impact your bottom line.
Our audience segmentation tools and processes can help with every kind of data grouping you want to explore. From geographic and behavioural to psychographic and beyond, our expert team can help you segment customers into their most useful and effective classifications.











